In the dynamic realm of data protection, understanding the consequences of non-compliance is crucial. The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act of 2023 has set forth stringent penalties for those who fail to adhere to its provisions.
We’ve delved into this new act in our series of blog posts. If you’re new to our site or have just come across our website, we highly recommend perusing our earlier posts, especially “Understanding the Basics of the DPDP Act,” for a thorough grasp of the DPDP Act.
However, if you’re a data controller or data fiduciary processing data in India or abroad involving Indian identities, compliance with the DPDP Act is mandatory.
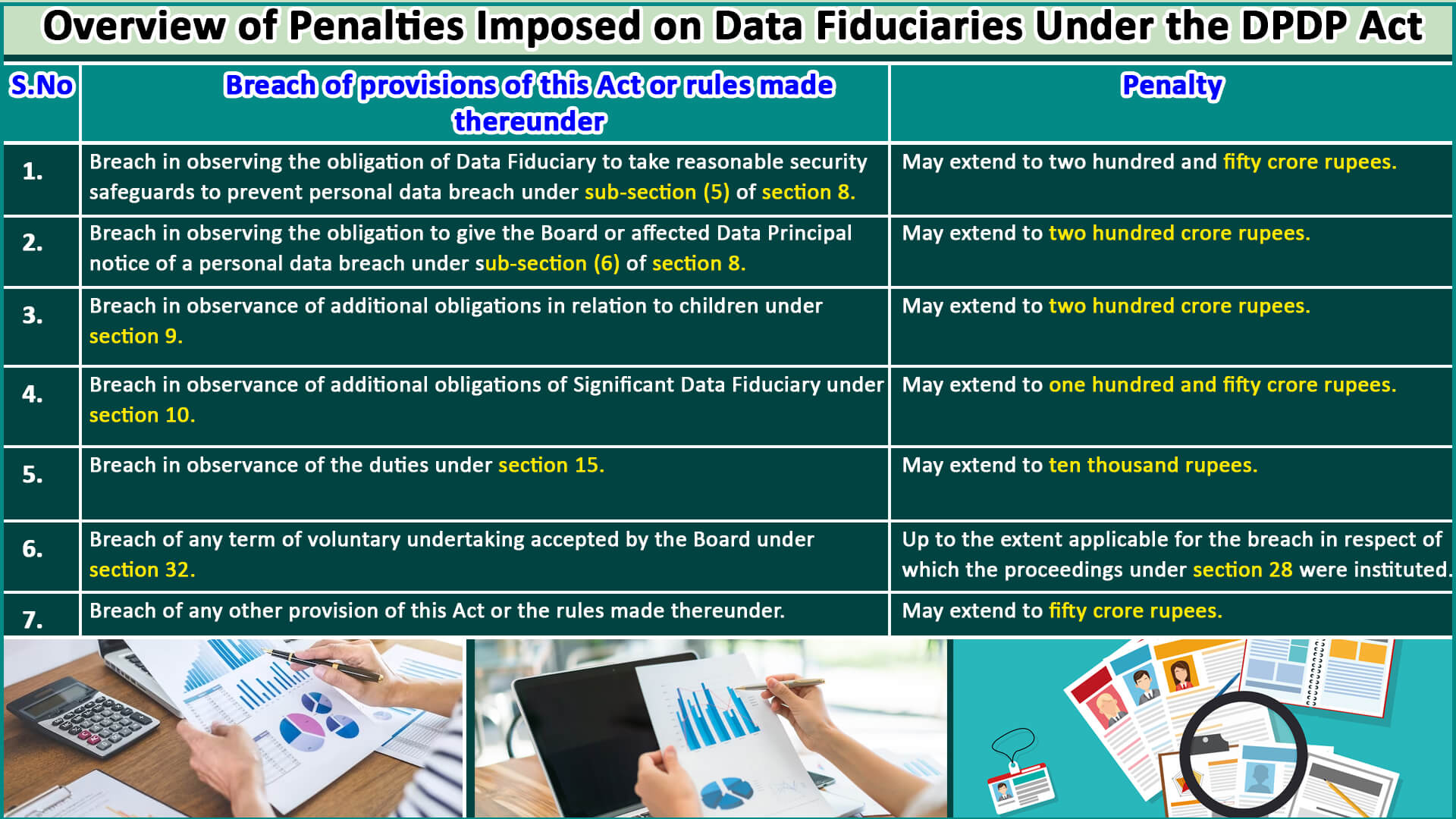
The penalties outlined in the table below underscore the Indian government’s steadfast commitment to data privacy.
This blog post is designed to shed light on these penalties and help you navigate the intricacies of the DPDP Act. So, without further ado, let’s dive in!
Authority of the DPDP Board: Penalties and Adjudication
Under Section 33 of the DPDP Act, the Digital Personal Data Protection Board (DPDPB) holds the authority to impose penalties on Data Controllers or Significant Data Fiduciaries (SDFs) for significant breaches of the Act or its rules (Clause 33 (1), DPDP Act).
However, it’s important to note that before any penalty is imposed, the party in question is given an opportunity to present their case. This ensures a process that is both fair and just, allowing for all sides to be heard before a final decision is made.
Assessing Penalties for Non-Compliance
In the process of determining the monetary penalty to be imposed under Section 33 (1), the Board takes into consideration several key factors. These include:
1.Nature, Gravity, and Duration of the Breach:
This refers to the breach’s nature, including its severity and duration. For example, a long-lasting breach exposing sensitive data is more serious than a minor, quickly rectified one.
2.Type and Nature of the Personal Data Affected:
The breach’s nature, particularly the type of personal data involved, is key. Breaches involving sensitive data like financial or health records typically attract higher penalties.
3.Repetitive Nature of the Breach:
If the breach is not a one-off incident and keeps recurring, it indicates a systemic issue within the data fiduciary’s systems that needs to be addressed. Such breaches could lead to higher penalties.
4.Gain or Loss Avoided as a Result of the Breach:
If the data controller has profited from the breach or avoided a loss, it will influence the penalty. This is to ensure that breaches do not result in any form of benefit for the responsible party.
5.Mitigation Efforts:
The Board will consider the data fiduciary’s mitigation efforts, including their timeliness and effectiveness. Swift and effective actions could potentially lower the penalty.
6.Proportionality and Effectiveness of the Penalty:
The Board ensures penalties are proportionate and effective in deterring future breaches, thus securing observance of the Act’s provisions and discouraging data controller violations.
7.Likely Impact of the Penalty on the Data Fiduciary:
The potential impact of the penalty on the data fiduciary responsible for the breach is also taken into account. This could include financial impact, reputational damage, and other relevant factors.
Where Do the Penalties Go?
All penalties imposed by the Board under this Act are credited to the Consolidated Fund of India. This ensures that the penalties serve a broader purpose and contribute to the nation’s financial resources.
Indeed, this is good news! However, it is strongly recommended that you comply with the DPDP Act to avoid any penalties. Read our blog on “How to Comply with the Principles of the DPDP”.
Conclusion
Grasping the implications of these penalties can empower individuals and organizations to adhere more effectively to the DPDP Act, thereby securing personal data and evading substantial penalties. As we journey through the digital world, it’s crucial to uphold the tenets of data protection and privacy. At VISTA InfoSec, we are committed to guiding you on this path. Our expertise and services can help you navigate the complexities of compliance, ensuring that your operations align with the DPDP Act. Let us help you turn data protection and privacy into a strategic advantage.